We have discussed earlier that, in general, you don’t need to count calories on a keto diet if you don’t have a tendency to overeat and are successfully shedding extra pounds. However, at the beginning of the keto diet, you still have to learn to count the calories and carbohydrates that you can eat during the day.
Having chosen a low-carb keto diet for yourself, you first need to understand the role, features, and effect on the body of carbohydrates. After all, keto is based on the principle of reducing carbohydrate foods and choosing the type of “good” vegetable carbs.
By consuming food, a person gets proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. The balance of these energy sources largely determines weight gain, keeping fit, and some health parameters. The keto diet involves a significant reduction in carbs to change the principle of metabolism. With a ketogenic diet, the body gets energy by breaking down fats. To achieve the goal, the body enters ketosis – a state in which ketone bodies are actively produced.
Ketosis is an unstable state that is easily broken by eating even a small amount of fast carbohydrates or exceeding the total amount of healthy carbohydrates for the day. But what is the correct way to count net carbs on keto?
Net carbs can be calculated by subtracting fiber and some sugar alcohols from total carbs. In the end, net carbs are those that your body can absorb and convert into energy. You don’t need to consider fiber because it is not processed by the body and does not raise blood sugar levels.
How do you figure out which carbs will benefit your body on keto and which are an obstacle to healthy ketosis? How to count net carbs on keto? Do you need to count fiber and other carbohydrates? At first glance, these questions seem very complicated, but we have all the answers. So let’s figure it all out together!
What Are Carbs?
What are carbohydrates? These are carbon hydrates – macronutrients consumed with food and serving as a source of energy. Carbohydrates are simple and complex. They are also called fast and slow, depending on the digestibility rate.
As your body digests carbohydrates, blood sugar rises. Due to the hormone insulin produced by the pancreas, glucose is absorbed by the body and converted into energy. In simple terms, carbohydrates can be called the easiest and most available fuel for the body. With a reduced intake of carbs, the body gets energy from proteins and fats, which is what happens on a keto diet.
In general, all carbohydrates can be divided into several simple groups [1].
Fiber
Fiber is a component of plants that cannot be digested by the human stomach but plays an important role in the metabolic process. It is essential for digestion and maintaining healthy blood sugar and cholesterol levels. It slows down the absorption of carbs. Your body does not digest fiber, but your gut microbiome uses it to perform many beneficial functions.
Fiber is found in various plant-based foods. Dietary fiber and high-fiber foods help avoid spikes in blood sugar. In addition, for people prone to uncontrolled weight gain, fiber is useful in preventing the formation of insulin resistance [2]. For this reason, it is the backbone of any diet.
Fiber is several types of complex carbohydrates with different chemical formulas. However, from a physical point of view, fiber is divided into water-soluble and water-insoluble. Although the body does not absorb both types of dietary fiber, the advantage of any high-fiber foods is their low glycemic index. Eating such foods helps maintain stable blood sugar levels [3].
Soluble fiber, found in fruits and some grains, becomes a gel-like substance in the stomach, serving as food for beneficial bacteria. In turn, coarse insoluble fiber improves the process of digestion.
Foods that are high in fiber have a low glycemic index. Insoluble dietary fiber in the stomach makes it difficult to digest carbohydrates, preventing their rapid assimilation. Such foods provide a long feeling of fullness. Dietary fiber fills the intestines, causing it to block the feeling of hunger and send a satiety signal to the brain, preventing overeating. Eventually, fiber slows down glucose absorption into the blood, positively affecting sugar and insulin levels.
Sugars
Simple, or easily digestible saccharides represent fast carbs. Often foods rich in fast carbohydrates have a noticeable sweet taste. After consuming fast carbohydrates, blood sugar levels rise sharply and quickly decrease due to the insulin produced. Therefore, foods based on fast carbohydrates have a high glycemic index.
The glycemic index is a relative measure of carbohydrates’ effect on raising blood sugar levels. The reference point for the glycemic index is the GI of sugar, which is 98-100. Therefore, the lower the GI value of food, the slower it is absorbed in your body, and the less it raises blood sugar.
Sugars have short chains of glucose molecules. Therefore, they are quickly absorbed and give a sharper increase in blood sugar. Sugars are contained in all vegetable, dairy, cereal, and legume foods. However, there are different concentrations and types of sugars. These can be milk or vegetable sugars.
Added sugar deserves special attention. Many foods contain added sugars such as cane sugar, beet sugar, glucose, dextrose, corn syrup, honey, and agave nectar. These sugars increase the total content of digestible carbs in foods and must be avoided during any diet.
 Starchy Carbohydrates
Starchy Carbohydrates
Compounds formed by glucose residues are slow or complex carbs. Foods based on slow carbohydrates have an unsweetened or slightly sweet taste and starchy or fibrous texture. These foods have a glycemic index of 50 or less.
During digestion in the gastrointestinal tract, starch slowly breaks down into pure glucose. Therefore, blood sugar does not rise sharply, and your body does not need to produce much insulin and convert excess glucose into fat. As a result, the blood sugar level remains almost the same for a long time, giving you the feeling of satiety for a long time.
Like simple carbs, starches give your body energy, but in greater amounts. Foods containing starch do not have a pronounced taste and are absorbed slowly, increasing blood glucose levels smoothly. High content of starchy carbohydrates is present in foods such as legumes, potatoes, rice, pasta, cereals, bread, etc.
Sugar Alcohols
Sugar alcohols, or as they are also called polyols [4], are a group of natural sugar substitutes that are contained, albeit in small quantities, for example, in fruits, berries, and cereals. They contain fewer calories per gram than sugar and do not cause cavities. The disadvantage of sugar alcohols is their laxative effect when taken in excess. However, they are safe for teeth, have a low glycemic index, and are fermented by the intestinal microflora.
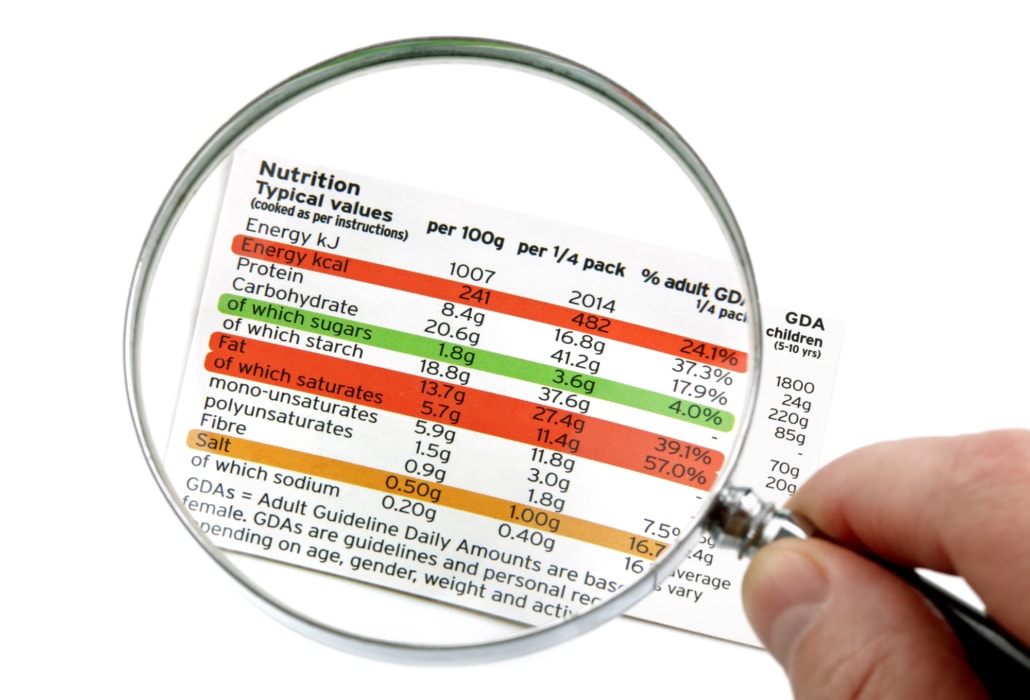
You can often find sugar alcohol on the nutrition label of low-carb foods. Sometimes they are listed separately in the nutritional value content, like this:
- Carbs – 9.8g
- Sugar alcohols – 8g
- Fiber – 1g
- Net carbs – 0.8g.
It is often tricky as not all sugar alcohols are keto-friendly, and some of them contain calories and raise blood sugar levels. However, you should know that there is a significant difference between sugar alcohols and regular carbohydrates. Regular carbohydrates, i.e., sugars, starch, etc., are almost completely hydrolyzed by enzymes in the duodenum and enter the bloodstream, causing an increase in glucose levels in it.
Sugar alcohols are not subject to the action of human digestive enzymes and enter the small intestine unchanged, where they are food for the microflora. Some of them are absorbed into the blood, and some are excreted without digestion.
The most common sugar alcohols are:
- erythritol
- sorbitol
- maltitol
- isomalt
- xylitol.
From our keto sweetener guide, you know that erythritol is the safest sweetener for the low carb diet. It contains no calories and does not raise your blood sugar levels [5]. At the same time, maltitol has 3-3.5 calories per gram and a GI of 35. Xylitol has 2.43 calories per gram and a GI of 13. For comparison, 1 gram of sugar contains 3.8 calories. As you can see, not all sugar alcohols are keto-friendly.
 How to Count Net Carbs on Keto?
How to Count Net Carbs on Keto?
The main principle of ketogenic nutrition is based on reducing the number of carbohydrates consumed. By reducing the number of carbs, the process of ketosis starts, helping your body to lose extra pounds. However, the incorrect consumption of even a small amount of carbohydrates can bring the body out of ketosis, thereby delaying the desired result.
On a keto diet, you need to consume a small number of complex carbohydrates from green vegetables and some berries. Fast carbs trigger increased insulin production, disrupting your ketosis. So it’s important to count net carbs at least at the beginning of your keto journey, avoiding hidden or added sugars.
In determining the appropriate ratio for yourself, it is important to clearly fit the number of carbohydrates consumed within the given limits. You need to precisely calculate all digestible carbohydrates. First of all, you should not ignore low-carb foods such as leafy vegetables, dairy, or nuts. After all, despite the fact that they contain few carbohydrates, your body digests them, affecting metabolism.
Counting the net carbs in complex meals is just as important as counting the ones you get with whole foods. For example, when cooking keto lasagna, you need to weigh all the ingredients and count the net carbs separately. In today’s world, it is very easy to do with the help of many apps that show you the net carbs of any meal and help you calculate complex dishes.
What Are Net Carbs?
So, in order to answer the main question of this post, it is worth clearly defining what net carbs are and how to count them. Net carbs are those carbohydrates that your body metabolizes and converts into energy. Typically, net carbohydrates include starchy carbohydrates and sugar (all kinds).
In other words, net carbohydrates are fully digestible carbs [6] that are found in food minus fiber. The fact is that fiber also contains carbohydrates, but they are not absorbed. The body does not digest fiber from whole foods, so carbs remain unprocessed. You can calculate net carbs using this formula:
Net carb calculation = total carb count – fiber
This formula is suitable for calculating net carbs from vegetables, fruits, and other whole foods. For example, 100g of kale contains 6g carbs-2g fiber=4g net carbs. Simple, right?
Your calculations may be complicated by additional lines on the label, such as added sugars or sugar alcohols. Added sugars are part of net carbs, so you can’t subtract them from the total. These are the pure sugars that raise your blood sugar levels. Yes, these are the sugars you need to avoid on keto, even in minimal amounts. If you see these words on the label, you should not consume this food while on keto.
Sugar alcohols can also complicate net carb calculations. As we have said above, some of them contain calories and provoke fluctuations in blood sugar, which means they need to be counted in the number of net carbohydrates. If out of 12g of total carbs, a meal contains 10g of sugar alcohols, and you see maltitol, xylitol, and other non-keto friendly options, that means net carbs would be 12g.
If the label has only erythritol without other sugar alcohols, but, for example, with zero-calorie stevia or monk fruit, then you can subtract the number of sugar alcohols from the total carbs and get 2 grams of net carbs. A little difficult, isn’t it? To keep things simple, I recommend that you avoid any food that contains sugar alcohols other than erythritol. This way, you will be sure it will not interrupt your ketosis.
Conclusion
The keto diet completely limits sugars and complex starchy carbs. To properly compose your menu, especially at the beginning of your keto weight loss journey, you need to learn how to count net carbs. To do this, you need to eliminate fiber from your total carbohydrate intake. The remaining grams are fully digestible carbohydrates, which should not exceed 20 grams daily. Besides, it should be healthy carbohydrates from vegetables, dairy, nuts, and other whole foods.
In the modern world, it’s very easy to count net carbs using various tables from the internet, calorie counting apps, and food labels. You should only count carbs at the beginning of your keto journey because later on, you will be able to intuitively understand how many net carbs a particular food contains.
Sources:
- Wheeler, M. L., & Pi-Sunyer, F. X. (2008). Carbohydrate issues: type and amount. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 108(4 Suppl 1), S34–S39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2008.01.024
- Lattimer, J. M., & Haub, M. D. (2010). Effects of dietary fiber and its components on metabolic health. Nutrients, 2(12), 1266–1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu2121266
- Nancy C. Howarth, M.Sc, Edward Saltzman, M.D., Susan B. Roberts, Ph D, Dietary Fiber and Weight Regulation, Nutrition Reviews, Volume 59, Issue 5, May 2001, Pages 129–139, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2001.tb07001.x
- Livesey, G. (2003). Health potential of polyols as sugar replacers, with emphasis on low glycaemic properties. Nutrition Research Reviews,16(2), 163-191.
- Ishikawa, M., Miyashita, M., Kawashima, Y., Nakamura, T., Saitou, N., & Modderman, J. (1996). Effects of oral administration of erythritol on patients with diabetes. Regulatory toxicology and pharmacology : RTP, 24(2 Pt 2), S303–S308. https://doi.org/10.1006/rtph.1996.0112
- Lilla, Z., Sullivan, D., Ellefson, W., Welton, K., & Crowley, R. (2005). Determination of “net carbohydrates” using high-performance anion exchange chromatography. Journal of AOAC International, 88(3), 714–719.